Covered under OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.120, Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response (HAZWOPER) training is mandatory for workers who handle hazardous substances, clean up contaminated sites, work at treatment and disposal facilities, or respond to hazmat emergencies. The training requirements vary significantly based on your specific job duties and exposure risk.
Who Needs HAZWOPER Training?
HAZWOPER applies to five types of operations under 29 CFR 1910.120(a)(1):
- Cleanup operations at uncontrolled hazardous waste sites (including EPA National Priority List sites)
- Corrective actions at RCRA sites
- Hazardous waste operations at treatment, storage, and disposal (TSD) facilities
- Emergency response operations involving hazardous substance releases (regardless of location)
- Voluntary cleanup operations at sites recognized by governmental bodies
Learn more in our latest blog Does Your Facility Need HAZWOPER Training? →
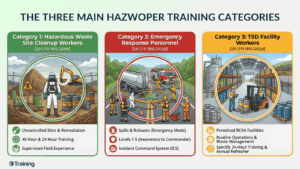
The Three Main HAZWOPER Training Categories
OSHA divides HAZWOPER training into three distinct categories based on work activities.
Category 1: Hazardous Waste Site Cleanup Workers [29 CFR 1910.120(e)]
This category covers general site workers, equipment operators, and supervisors engaged in cleanup operations at uncontrolled hazardous waste sites. These aren’t emergency responders, they’re the crews doing remediation work.
40-Hour HAZWOPER [29 CFR 1910.120(e)(3)(i)]
Who needs it: General site workers (laborers, equipment operators, supervisors) who are exposed or potentially exposed to hazardous substances above permissible exposure limits.
Training requirement: Minimum 40 hours of off-site instruction PLUS three days of mandatory actual field experience under direct supervision of a trained, experienced supervisor.
24-Hour HAZWOPER [29 CFR 1910.120(e)(3)(ii) and (e)(3)(iii)]
Who needs it:
- Occasional site workers performing specific limited tasks (groundwater monitoring, land surveying, geophysical surveying) who are unlikely to be exposed above permissible limits
- Regular workers on fully characterized sites where exposures are documented to be below permissible limits and respirators aren’t necessary
Training requirement: Minimum 24 hours of off-site instruction PLUS one day of mandatory actual field experience under direct supervision. Workers with 24-hour training who later become general site workers or are required to wear respirators must complete an additional 16 hours of training plus two more days of field experience to meet the full 40-hour requirement.
Category 2: Emergency Response Personnel [29 CFR 1910.120(q)]
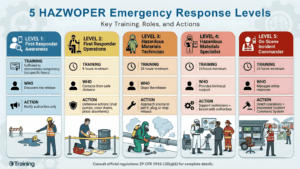
Under 29 CFR 1910.120(q)(6), OSHA defines five levels of emergency response training. Each level corresponds to specific responsibilities during a hazardous materials incident:
Level 1: First Responder Awareness Level [29 CFR 1910.120(q)(6)(i)]
Who needs it: Employees who are likely to witness or discover a hazardous substance release during their regular duties – warehouse workers, lab techs, or facility personnel who aren’t part of a hazmat team.
What they do: Recognize that a release has occurred, initiate the emergency response sequence, and notify proper authorities. They take NO further action beyond notification.
Training requirement: Sufficient training or experience to demonstrate competency in:
- Understanding what hazardous substances are and their associated risks
- Recognizing hazardous materials in an emergency
- Understanding their role in the emergency response plan
- Knowing when to call for additional resources
Level 2: First Responder Operations Level [29 CFR 1910.120(q)(6)(ii)]
Who needs it: Personnel who respond to releases in a defensive manner to protect people, property, and the environment.
What they do: Take defensive actions from a safe distance to contain the release and prevent it from spreading. They do NOT attempt to stop the release.
Training requirement: Minimum 8 hours of training or equivalent work experience demonstrating competency in:
- Basic hazard and risk assessment techniques
- Hazmat terminology
- Selection, use, and limitations of personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Basic containment, control, and confinement operations
- Basic decontamination procedures
Level 3: Hazardous Materials Technician [29 CFR 1910.120(q)(6)(iii)]
Who needs it: Emergency response technicians who take aggressive action to stop the release.
What they do: Approach the point of release to patch, plug, or otherwise stop it. They work hands-on with leaking containers, damaged pipes, or compromised storage vessels.
Training requirement: Minimum 24 hours of training (including all competencies from Operations Level) plus demonstration of competency in:
- Implementing emergency response plans
- Classification, identification, and verification of materials using field survey instruments
- Functioning within the Incident Command System (ICS)
- Selection and use of specialized chemical protective equipment
- Advanced hazard and risk assessment techniques
- Performing advanced containment, control, and confinement operations
- Understanding and implementing decontamination procedures
- Basic chemical and toxicological terminology and behavior
Level 4: Hazardous Materials Specialist [29 CFR 1910.120(q)(6)(iv)]
Who needs it: Responders who provide technical support to hazmat technicians and act as the site liaison with federal, state, and local authorities.
What they do: Perform duties parallel to technicians but in a knowledge-based support role. They bring specialized expertise in specific hazardous substances and serve as the technical point of contact with outside agencies.
Training requirement: Minimum 24 hours of training (equivalent to Technician Level) with demonstrated competency in:
- Implementing local and state emergency response plans
- Advanced classification and identification using specialized survey instruments
- In-depth hazard and risk assessment techniques
- Specialized control and confinement operations
- Determining and implementing decontamination procedures
- Developing site safety and control plans
- In-depth chemical, radiological, and toxicological knowledge
Level 5: On-Scene Incident Commander [29 CFR 1910.120(q)(6)(v)]
Who needs it: The person responsible for overall management of the hazmat emergency response.
What they do: Direct all response activities, implement the Incident Command System, develop strategy, and coordinate with local, state, and federal response teams.
Training requirement: Minimum 24 hours of training (many complete the full 40-hour course) equivalent to Operations Level plus demonstrated competency in:
- Implementing the employer’s Incident Command System
- Understanding hazards and risks of employees working in chemical protective clothing
- Implementing local emergency response plans
- Knowledge of state emergency response plan and Federal Regional Response Team
- Understanding decontamination procedures
Category 3: TSD Facility Workers [29 CFR 1910.120(p)(7)]
This category covers employees working at Treatment, Storage, and Disposal (TSD) facilities regulated by EPA under RCRA. These are permanent facilities (not emergency response sites or temporary cleanup operations) that handle hazardous waste as part of ongoing operations.
Who needs it: Employees at TSD facilities who are exposed to health hazards or hazardous substances at the facility.
Training requirement: 24 hours of initial training plus 8 hours of annual refresher training. The training must enable employees to perform their duties safely and cover topics specific to the hazards at their facility.
Annual Refresher Training Requirements
All HAZWOPER-trained workers must complete annual refresher training:
For site cleanup workers [29 CFR 1910.120(e)(8)]: 8 hours of refresher training annually for those who completed 24-hour or 40-hour initial training.
For emergency responders [29 CFR 1910.120(q)(8)]: Annual refresher training of sufficient content and duration to maintain competencies, or demonstration of competency at least yearly.
For TSD facility workers [29 CFR 1910.120(p)(7)(i)]: 8 hours of refresher training annually.
Need HAZWOPER training for your team?
eTraining offers comprehensive online HAZWOPER courses including 8-hour annual refreshers, 24-hour, and 40-hour initial training. Our courses meet all OSHA requirements under 29 CFR 1910.120 and are updated annually to reflect current regulations.
Wondering What HAZWOPER course applies for your job role?
Answer 3-4 quick questions about your operation type, role, and exposure scenarios and we’ll provide an accurate recommendation based on OSHA regulations for the training that applies to you. Takes 2 minutes, saves thousands in training costs or penalties.